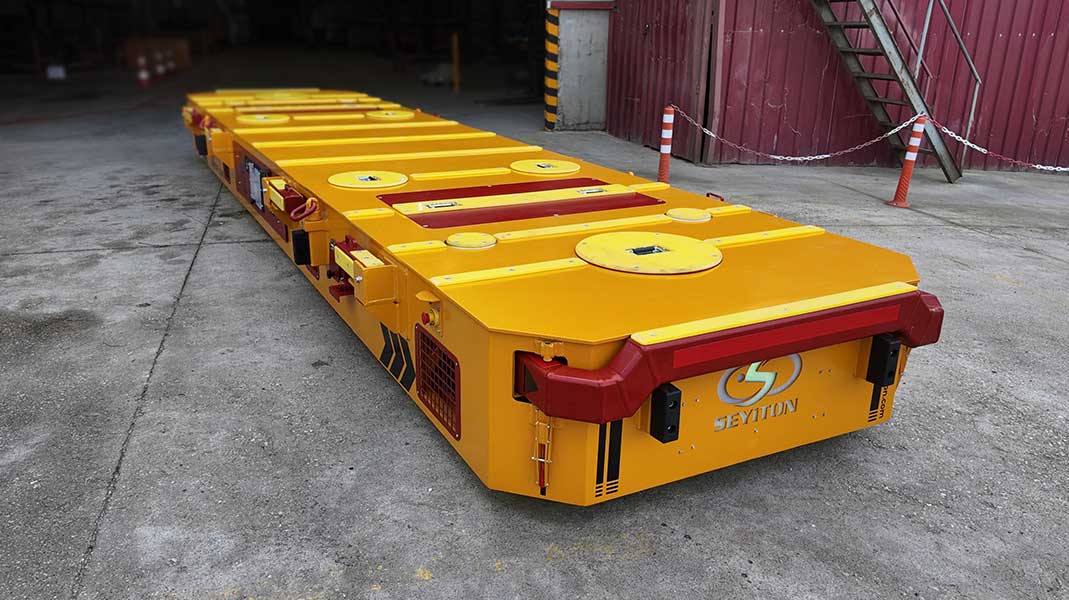
Steerable transfer carts are heavy-duty, wheel-based vehicles designed to move extremely heavy loads across your facility without any rail infrastructure. Operating directly on flat industrial floors such as concrete or asphalt, they can be driven to any required point inside the plant instead of being limited to fixed stations or routes. This gives engineering, maintenance and production teams far more freedom when planning material flow and future layout changes.
Unlike traditional rail carts, which are tied to predefined tracks, battery powered transfer carts follow the paths defined by your process – not the other way around. They are especially valuable in plants where products, lines or equipment are frequently rearranged, or where installing rails is technically difficult, costly or disruptive. Combined with zero-emission battery power and advanced steering options, they offer a modern alternative to rail-guided transfer carts, forklifts and overhead cranes for repetitive heavy-load movements.
In practice, steerable transfer carts allow you to:
- Uninterrupted Energy: Ensure long-range operation with high-capacity battery power, without the need for cables or rail lines. (For more information about batteries, you can review our Battery Comparison Guide.)
- Infrastructure-Free Installation: Transport heavy loads without laying rails or incurring construction costs.
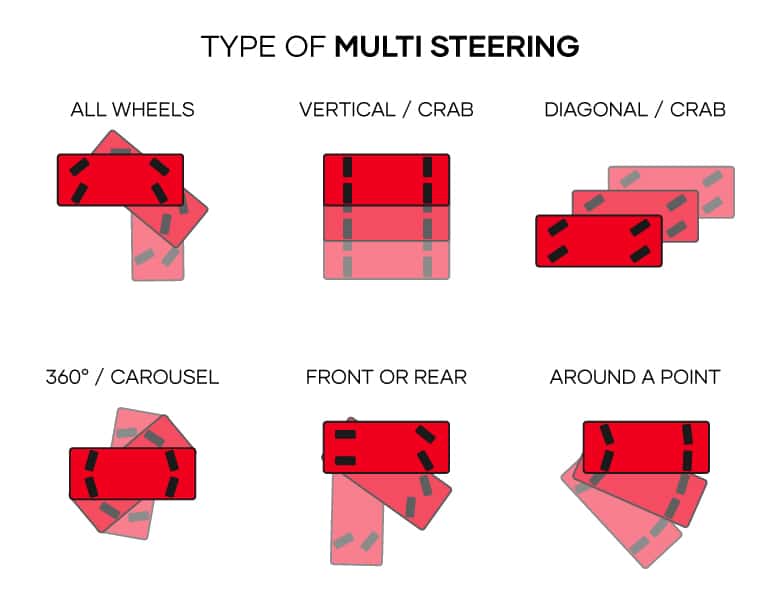
- High Maneuverability: Perform complex movements such as crab steering and rotation on the spot even in the tightest spaces, thanks to the next-generation wheel modules we have developed, enabling precise positioning.
- Full Access: Reach any point in the facility, not just fixed stations.
- Flexible Layout: Instantly adapt material flow when your production processes change.
Advantages of Steerable Transfer Carts
The greatest advantage of steerable transfer carts is their flexibility and ease of deployment. They can be operated immediately on existing factory floors without the need for any modifications to the facility’s infrastructure. These carts can travel along various routes and reach any desired point, making them easily adaptable to changes in the production flow. It is possible to change loading and unloading locations or assign the vehicle to different tasks as needed. Models with high maneuverability can successfully operate in tight spaces or corridors requiring 90° turns. Additionally, two or more transfer carts can be used in a synchronized manner to transport a single large load together—allowing long or wide materials that cannot be handled by a single cart to be moved efficiently through coordinated operation.
Why Choose Seyiton for Steerable Transfer Cart Projects?
At Seyiton, we combine engineering expertise, manufacturing capabilities and field experience to deliver reliable heavy-duty transfer cart solutions. Our engineering team is experienced in trackless and steerable carts and designs each project around your load, layout and safety requirements. With proven solutions for loads up to 500 tons and a strong focus on safety – from braking systems and steering control to alarms and sensors – we support you throughout the entire lifecycle of the system, from design and manufacturing to commissioning and after-sales. In this way, you don’t just invest in a single piece of equipment, but in a long-lasting system that supports your plant’s heavy load handling strategy.
Project Videos
Questions About Our Steerable Transfer Carts
It is a heavy-duty, steerable transfer cart that moves freely on flat factory floors without rails and is powered by onboard industrial batteries. It is designed to carry very heavy loads safely and repeatedly inside the plant.
We engineer our steerable carts for loads of up to 500 tons. The exact capacity is defined project by project, based on your load, floor conditions and required safety margins.
Runtime depends on load, travel distance and how intensively the cart is used. We size the LiFePO4 battery packs and define a charging strategy (overnight, opportunity or swapping) so that the cart can support your daily operating cycle reliably.
In most heavy-duty applications, the cart is operated via wireless remote control, so the operator walks next to the load and keeps a clear view of the surroundings. If your process requires it, we can also add an onboard cabin or control panel, but remote operation is generally the safest and most flexible option.
Yes. We don’t just deliver the cart; we also support you with installation planning, on-site commissioning and operator training, so your team can start using the system safely and efficiently from day one.